Introduction
Virgil Security provides a set of APIs for adding security to any application or IoT device.
Virgil IoTKit is a C library for connecting IoT devices to the Virgil IoT Security Platform. IoTKit helps you easily add security to your IoT devices at any lifecycle stage for securely provisioning and authenticating devices, updating firmware and TrustLists, and exchanging messages using any transport protocols.
Content
- Features
- IoT Dev Tools
- Run IoTKit Sandbox
- IoTKit Modules
- Scripts
- Installation
- Tests
- IoTKit Usage
- API Reference
- License
- Support
Features
Virgil IoTKit provides a set of features for IoT device security and management:
- Crypto Module. Connect any crypto library and Security Module. Virgil IoTKit provides a flexible and simple API for any types of crypto library and SECMODULE. The framework also provides default Software Security Module implementation based on the Virgil Crypto Library. (Support for ATECC608A and ATECC508A in the next version).
- Provision Module. Secure IoT device provision. In order to securely update firmware and securely register, authenticate or exchange messages between IoT devices, each IoT device must have its own tools that allow the device to perform cryptographic operations. These tools must contain information needed to identify the device or other participants (e.g. the TrustList provider). These tools are the device keys, TrustLists, device card, etc. The process of providing your IoT devices with these tools is called device provisioning, and Virgil IoTKit gives you all the functionality needed to make your IoT devices identifiable and verifiable, as a result, protected from counterfeiting and fabrication.
- Firmware Module. Secure firmware and TrustList verification and distribution. IoTKit provides a set of APIs for secure verification of firmware in a bootloader. Also, IoTKit provides an example of bootloader implementation in the form of emulator.
- Secbox Module. Secure storage software for any sensitive data. IoTKit provides secure storage software that is called Secbox for storing any sensitive data, like private keys. The Secbox works in two modes; the first mode - when data is only signed, and the second one - when data is encrypted and then signed.
- Protocols Module. IoTKit provides a flexible, programmable security network adaptive protocol (SNAP) for device-to-device, device-to-cloud, and cloud-to-device communication. SNAP can be used for secure firmware distribution, secure notification about device state, and secure device provision. Also, SNAP contains a set of functions and interfaces that allows you to work with any transport protocol (BLE, Wi-Fi, PLC, NoiseSocket, etc.).
- Cloud Module. API for working with the Virgil IoT Security Platform. IoTKit interacts with the Virgil IoT Security Platform to provide you with the services for the security, management, and monitoring of IoT devices.
- Logger Module. IoTKit contains a set of functions and interfaces for logging device events.
- C/C++ support. Library is implemented on C99. There is C++ integration based on Qt crossplatform library. Also there are tools implemented on Golang.
IoT Dev Tools
Virgil Security also provides a set of tools for secure device lifecycle:
- Virgil Trust Provisioner. The Virgil Trust Provisioner is a CLI used to manage your distributed trust between all parties, including IoT devices, in your IoT solutions. The CLI is aimed at key pairs and TrustList generation and management, which together make each IoT device identifiable, verifiable and trusted by each party of IoT solution. To start working with the tool, read more here.
- Virgil Device Initializer. In order to make each IoT device identifiable, verifiable and trusted by each party of IoT solution, you have to provide it with specific provision files, generate private keys and create the digital cards for further device registration on the Virgil Cloud. Virgil Device Initializer allows you to make IoT device provisioning and prepare your IoT device (create digital cards) for its further registration on the Virgil Cloud. To start working with the tool, read more here.
- Virgil Device Registrar. Virgil IoT Device Registrar is used to register IoT devices and their digital cards with the Virgil Security Cloud. To start working with the tool, read more here.
- Virgil Firmware Signer. Virgil Firmware Signer is a CLI that allows you to sign firmware in order to provide integrity before distributing it. To start working with the tool, read more here.
- Virgil SnapD. Virgil SnapD is a local web utility which allows you to obtain information and statistics about your IoT devices. In order to get such device information, SnapD interacts with Virgil SNAP protocol, which operates directly with your IoT devices. As far as Virgil SnapD is a local service, the obtained information can be displayed in browser under http://localhost:8080/ (by default). If you're working with the Virgil IoT Simulator, you can run SnapD under http://localhost:8081/. To start working with the tool, read more here.
Run IoTKit Sandbox
To demonstrate our IoTKit in action we developed Sandbox based on IoTKit.
The Sandbox is conditionally divided into 3 actors (Vendor, Factory and End-user) and shows the secure lifecycle of IoT devices. The Sandbox allows you to:
- Generate trusted provisioning package. To start working with emulated IoT infrastructure, the Sandbox uses Virgil Trust Provisioner utility for generating provisioning files, such as private keys (e.g. for factory, firmware) and a distributed TrustList that contains public keys and signatures of trusted service providers (e.g. factory, cloud).
- Emulate IoT devices. Then, you can emulate two IoT device types: IoT Gateway - an internet-capable smart device that communicates with other IoT devices and the Virgil Cloud; and IoT Device - edge device, like smart bulb, that can be controlled remotely through the IoT Gateway.
- Securely perform IoT device provisioning. Sandbox uses the Virgil Device Initializer for IoT devices provisioning to make them identifiable, verifiable and trusted. Securely integrate TrusList into IoT device, then generate key pair and create digital card, and sign digital card with the device key.
- Register IoT devices on the security platform. On this step, the Virgil Device Registrar is used to register digital cards of IoT devices with the Virgil Cloud for further device authentication and management.
- Sign and publish new Firmware and TrustList. Also, you can emulate the process of creating and publishing new Firmware or TrustList to Virgil Cloud. Sandbox uses Virgil Firmware Signer to sign a firmware before its distributing.
- Manage IoT devices. Sandbox allows you to manage IoT devices and get information about their state. Sandbox uses Virgil services to notify IoT devices about new updates and then securely verify incoming firmware or TrustLists before updating them.
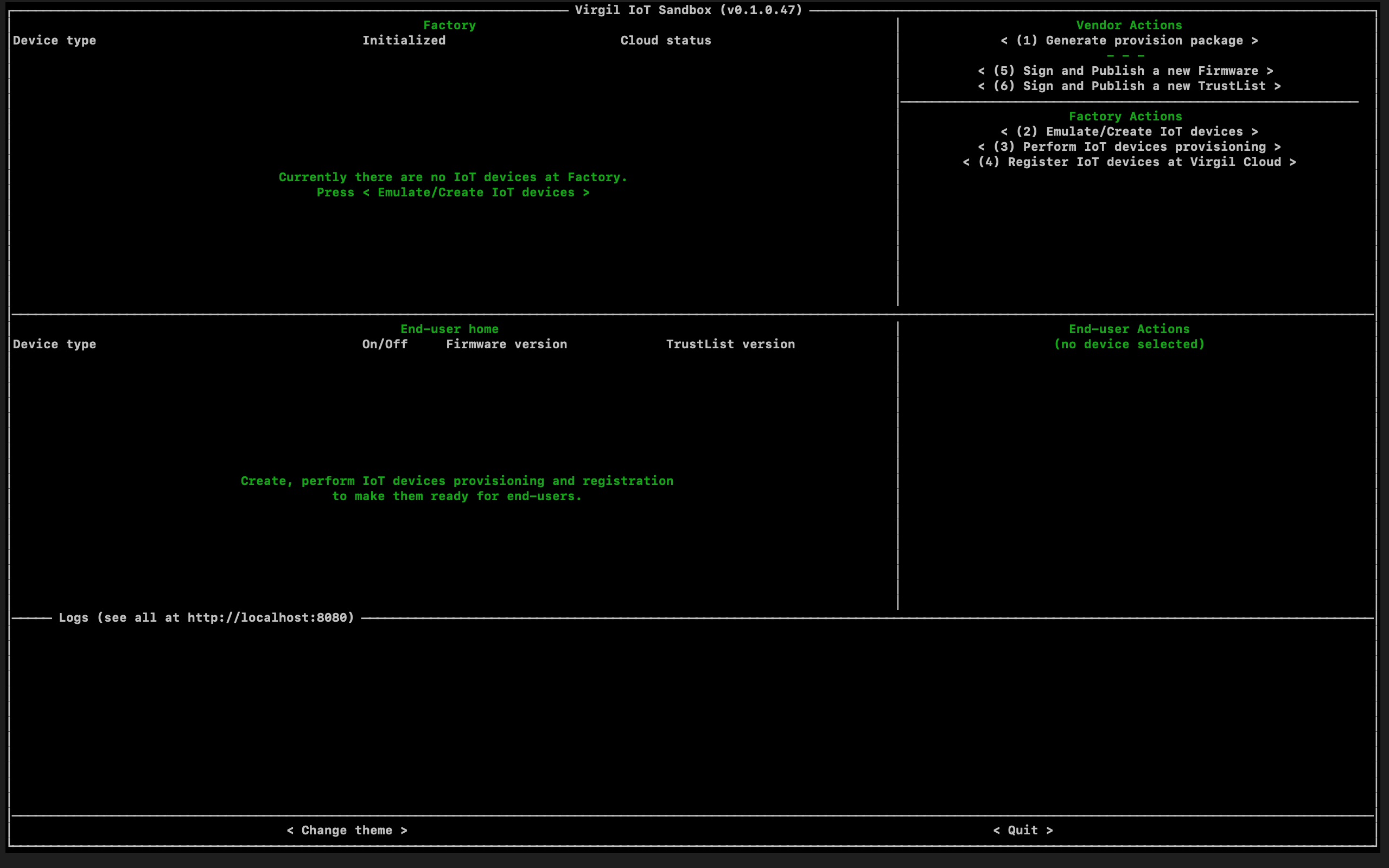
To start working with the Sandbox follow Sandbox README.
You can try to use Demo IoTKit Qt open project on your platform to test Qt integration usage. This software grants you modern GUI application able to be started on many desktop and mobile platforms like Linux, Windows, Android, iOS etc.
IoTKit Modules
As we mentioned above, Virgil IoTKit provides a set of features that implemented to modules:
- Cloud Module is used for for obtaining credentials from Virgil Thing service and downloading firmware images and TrustList files from cloud storage.
- Crypto Module is used for cryptographic operations with callbacks for Software Security Module and cryptographic converters.
- Firmware Module is used for firmware downloading, uploading and processing by IoT Gateway or by Thing (IoT Device).
- Logger is a tool is used to output logging messages to screen, file etc.
- Provision. TrustList keys reading and verifying.
- Secbox is a secure data storage wth signing and authenticating abilities.
- Protocols Module provides the set of services for SNAP protocol:
- INFO: service for collecting statistics from devices. See INFO Server and INFO Client
- FLDT: service for files download from Gateway to Thing. See FLDT Server and FLDT Client
- PRVS: service for make provision for device by factory initializer. See PRVS Server and PRVS Client
Scripts
Virgil IoTKit also contains a set of scripts that can be run from the scripts folder.
run-sandboxis used to run IoTKit sandbox. Read more about the sandbox and its functionality here.publish-firmware.shis used to publish a signed firmware on the Virgil Cloud for its distribution to IoT devices. Read more about firmware distribution here.publish-trustlist.shis used to publish a generated TrustList on the Virgil Cloud for its distribution to IoT devices. Read more about TrustLists distribution here.build-for-qt.shis used to generate Virgil IoTKit libraries for different platform. If you run this script without parameters, it will output all supported platforms. Usage examples :- To get a library for Android :
ext/virgil-iotkit/scripts/build-for-qt.sh android armeabi-v7a - To get a library for iOS :
ext/virgil-iotkit/scripts/build-for-qt.sh ios - To get a library for iOS-simulator:
ext/virgil-iotkit/scripts/build-for-qt.sh ios-sim - To get a library for Linux :
ext/virgil-iotkit/scripts/build-for-qt.sh linux - To get a library for MacOS :
ext/virgil-iotkit/scripts/build-for-qt.sh macos - To get a library for Windows by using mingw32 on another host platform :
ext/virgil-iotkit/scripts/build-for-qt.sh mingw32 - To get a library for Windows :
ext/virgil-iotkit/scripts/build-for-qt.sh windows. See Windows installation for running script details.
- To get a library for Android :
Installation
Virgil IoTKit is distributed as a package. This section demonstrates on how to install Virgil IoTKit for preferred platform.
Prerequisites
To start working with Virgil IoTKit the following components are required:
- C99 for C.
- CMake v3.11 or higher, for project building
- GCC or another toolchain for C/C++ compile
- Golang to compile Virgil IoT dev tools
- git for Virgil Crypto installation and update
- curl for default NIX implementation
Also Virgil IoTKit has C++/Qt integration based on Qt crossplatform library. Following components are required to use Qt integration:
- C++14.
- Qt 5.12.6 or higher.
- Qt built for your target platform: Android, iOS, Linux, MacOS, Windows etc.
Ubuntu, Debian, Raspbian OS
To download and install the Virgil IoTKit on Ubuntu, use the following command:
To add repository to preferred OS, use the following command:
Ubuntu 19.10 Suite (eoan)
Ubuntu 18.04 (bionic)
Raspbian 9 (stretch)
Raspbian 10 (buster)
Note! All DEB repositories are not signed, therefore to update lists for them use the following command: apt-get update --allow-insecure-repositories --allow-unauthenticated
Fedora OS
To download and install the Virgil IoTKit on Fedora or CentOS, use the following command:
To add repository to preferred OS use the following command:
Fedora 29
Fedora 30
Fedora 31
MacOS
To download and install the Virgil IoTKit on MacOS, use the following command:
Windows OS
It is necessary to install software listed below :
- Git for Virgil IoTKit components installation and upgrade.
- CMake as Virgil IoTKit framework build system.
- make. It can be installed separately from GNUWin32 project. Also it contains in mingw compiler.
- MSYS2 as shell commands interpreter
- mingw-w64 as C/C++ compiler. It is suggested to use mingw to use GCC bytes alignment in packet structures.
- Also you can install Qt that will be used for Qt integration. Qt Maintenance Tool installs mingw, CMake and make.
Start MSYS2 and try to see all those software versions :
If some software has not been found, check PATH system variable.
After these steps you can clone Git repository and use build-for-qt.sh script.
Qt integration
- Setup Qt with your target platforms support. Each platform has its own requirement. See Qt documentation for details.
- Compile Virgil IoTKit library for target platform. See Scripts section,
build-for-qt.shscript description for details. - Build and deploy application.
Tests
To make sure that everything goes in the right way, we also provide a set of ready code-snippets for testing all the required features:
- Crypto: crypto algorithms (e. g. hash, RNG, AES) and crypto operations (key pair, sign/verify etc.).
- Firmware related functionality: create firmware, save/load/install.
- Security Box (test storage module): read write for signed or/and encrypted data.
- SNAP (Secure Network Adjustable Protocol tests): send, receive etc.
Navigate to the tests folder of our IoTKit Demo repository to find preferred tests and start working with them.
You can try to use Demo IoTKit Qt open project to test Qt integration usage. To have full testing start any IoT devices in your network and observe its states by using demo-iotkit-qt software. You can use Sandbox as such devices set.
IoTKit Usage
To start working with Virgil IoTKit you have to:
- specify configuration parameters.
- provide implementations (you can also use default implementations).
Configuration parameters
Configuration headers directory
There are configuration headers that customize Virgil IoTKit, they are stored in config directory. You can provide your headers or use standard ones. It's necessary to add VIRGIL_IOT_CONFIG_DIRECTORY variable that points to the directory with configuration files.
For example, if you want to use PC configuration provided by library and library is stored in
virgil-iotkitdirectory, you have to set compiler option:-DVIRGIL_IOT_CONFIG_DIRECTORY virgil-iotkit/config/pc.
MCU Build
The VIRGIL_IOT_MCU_BUILD variable enables or disables microcontroller features. If some microcontroller features are not compatible with your PC configuration or you don't need to use MCU features, you can disable them through the VIRGIL_IOT_MCU_BUILD variable during compilation: -DVIRGIL_IOT_MCU_BUILD=OFF.
Mobile platforms Build
Use integration/qt/iotkit.pri qmake script to include Virgil IoTKit Qt framework.
Mandatory implementations
Some IoTKit modules use external implementations, therefore it's necessary to implement HAL (hardware abstraction layer) functions:
- Storage context: structure vs_storage_op_ctx_t contains external data operations like open/read/write/close. See Storage HAL for details.
- Firmware: vs_firmware_install_prepare_space_hal, vs_firmware_install_append_data_hal and vs_firmware_get_own_firmware_footer_hal functions have to be implemented for firmware processing. See Firmware HAL for details.
- Logger: depends on logger-config.h configurations vs_logger_output_hal for string output and/or vs_logger_current_time_hal for current time output. See Logger HAL for details.
- SNAP protocol: vs_netif_t network interface as transport level for SNAP protocol. As UDP broadcast example user can use c-implementation tool. See SNAP Reference for details.
- FLDT Server is a service that is used by a IoT Gateway for files (e.g. firmware, TrustLists) distribution for IoT devices. Server sends new files in the network to IoT Devices and processes Client requests for new files.
- FLDT Client is client for FLDT service that used by IoT Devices to receive new files (e.g. Firmware, TrustLists) from IoT Gateway. FLDT Client also can request files versions.
- PRVS Client: there is a need to implement vs_snap_prvs_client_impl_t structure. This structure contains wait functions for SNAP interface. You can see example of implementation in the c-implementation.
Default Mandatory implementations
Virgil IoTKit also provides default mandatory implementations:
- Cloud : vs_cloud_impl_t and vs_cloud_message_bin_impl_t are required
by vs_cloud_init. Functionvs_curl_http_implreturns cURL HTTP implementation,vs_cloud_message_bin_impl_treturns MQTT implementation. - Crypto introduces security module implementation structure vs_secmodule_impl_t. Function
vs_soft_secmodule_implreturns software implementation.
API Reference
License
This library is released under the [3-clause BSD License](LICENSE).
Support
Our developer support team is here to help you. Find more information on our Help Center.
You can find us on Twitter or send us an email at support@VirgilSecurity.com.
Also, get extra help from our support team on Slack.

 1.8.17
1.8.17